Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin C

Vitamin C is an essential nutrient required for the maintenance of many body tissues, including skin, blood vessels, bones, and cartilage. Vitamin C is also essential for wound healing. (1,2)
Vitamin C helps protect cells against oxidative stress, which in turn provides protection against certain diseases, including cancer. (1,3)
Vitamin C, like zinc and vitamin A, also helps support your immune system. (4,5,6)
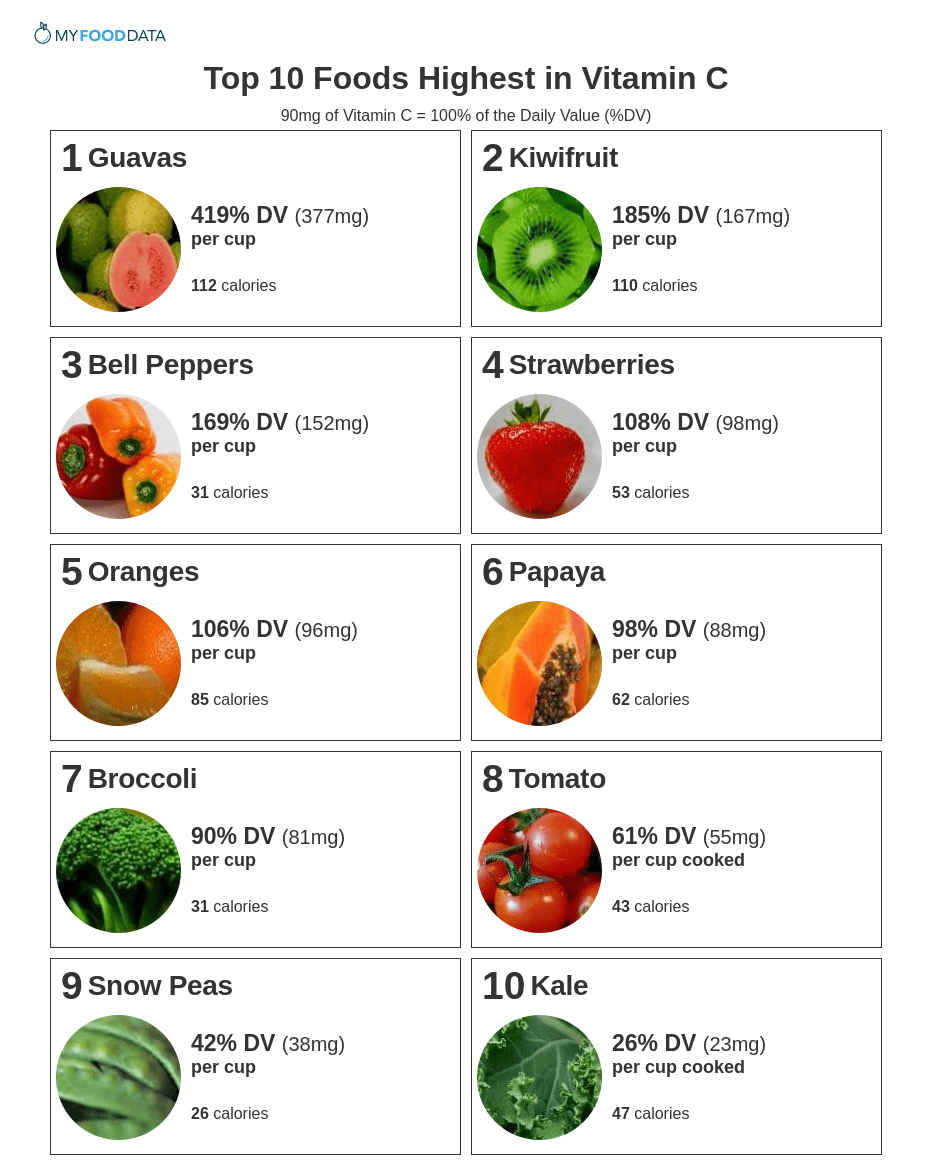
High vitamin C foods include guavas, bell peppers, kiwifruit, strawberries, oranges, papayas, broccoli, tomatoes, kale, and snow peas. The current daily value (DV) for vitamin C is 90mg. (7)
Below is a list of high vitamin C foods ranked by a common serving size. Use the nutrient ranking of over 200 foods high in vitamin C to see the foods highest in vitamin C by nutrient density (per gram), or see rankings of fruits high in vitamin C, and vegetables high in vitamin C.
High Vitamin C Foods
 1 Guavas
1 Guavas| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 377mg (419% DV) | 228mg (254% DV) | 671mg (746% DV) |
See all fruits high in vitamin C.
 2 Kiwifruit
2 Kiwifruit| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 167mg (185% DV) | 93mg (103% DV) | 304mg (338% DV) |
 3 Bell Peppers
3 Bell Peppers| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 152mg (169% DV) | 128mg (142% DV) | 982mg (1091% DV) |
Red bell peppers provide around 50% more vitamin C than green bell peppers. View the complete comparison of green vs red bell peppers.
 4 Strawberries
4 Strawberries| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 98mg (108% DV) | 59mg (65% DV) | 368mg (408% DV) |
More Berries High in Vitamin C
- 36% DV in 1 cup of raspberries
- 34% DV in 1 cup of blackberries
- 16% DV in 1 cup of blueberries
See all fruits high in vitamin C.
 5 Oranges
5 Oranges| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 96mg (106% DV) | 53mg (59% DV) | 226mg (252% DV) |
More Citrus Fruit High in Vitamin C
- 413% DV in 1 pomelo
- 98% DV in 1 grapefruit
- 40% DV in 1 clementine
- 34% DV in 1 lemon
 6 Papaya
6 Papaya| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 88mg (98% DV) | 61mg (68% DV) | 283mg (315% DV) |
More Tropical Fruits High in Vitamin C
- 88% DV in 1 cup of pineapple
- 72% DV in 1 cup of cantaloupe melon
- 67% DV in 1 cup of sliced mango
- 34% DV in 1 cup of honeydew melon
See all fruits high in vitamin C.
 7 Broccoli
7 Broccoli| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 81mg (90% DV) | 89mg (99% DV) | 525mg (583% DV) |
More Brassica Vegetables High in Vitamin C
- 107% DV in 1 cup of brussels sprouts
- 61% DV in 1 cup of cauliflower
- 63% DV in 1 cup of cabbage
See all vegetables high in vitamin C.
 8 Tomato
8 Tomato| Vitamin C per Cup Cooked | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 55mg (61% DV) | 23mg (25% DV) | 253mg (281% DV) |
 9 Snow Peas
9 Snow Peas| Vitamin C per Cup | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 38mg (42% DV) | 60mg (67% DV) | 286mg (317% DV) |
 10 Kale
10 Kale| Vitamin C per Cup Cooked | Vitamin C per 100g | Vitamin C per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 23mg (26% DV) | 18mg (20% DV) | 99mg (110% DV) |
More Green Leafy Vegetables High in Vitamin C
- 44% DV in 1 cup of turnip greens
- 35% DV in 1 cup of Swiss chard
- 20% DV in 1 cup of spinach
See all vegetables high in vitamin C.
Printable One Page Sheet
Vitamin C Foods by Nutrient Density (Vitamin C per Gram)
| Food | Serving | Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Acerola Cherry | 100 grams | 1864% DV (1678mg) |
| 2 Dried Herbs (Coriander) | 100 grams | 630% DV (567mg) |
| 3 Rose Hips | 100 grams | 473% DV (426mg) |
| 4 Guavas | 100 grams | 254% DV (228mg) |
| 5 Sweet Yellow Peppers | 100 grams | 204% DV (184mg) |
| 6 Black Currants | 100 grams | 201% DV (181mg) |
| 7 Thyme | 100 grams | 178% DV (160mg) |
| 8 Red Chilies | 100 grams | 160% DV (144mg) |
| 9 Scotch Kale | 100 grams | 144% DV (130mg) |
| 10 Kiwifruit | 100 grams | 103% DV (93mg) |
Other Vitamin C Rich Foods
| Food | Serving | Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Litchis (Lychees) | per cup | 151% DV (136mg) |
| 2 Green Chillies | 1 pepper | 121% DV (109mg) |
| 3 Kohlrabi | 1 cup | 93% DV (84mg) |
| 4 Parsley | per cup | 89% DV (80mg) |
| 5 Orange Juice | per 8oz cup | 80% DV (72mg) |
| 6 Bitter Melon | per cup | 45% DV (41mg) |
| 7 Starfruit (Carambola) | per cup | 41% DV (37mg) |
| 8 Garden Cress | 1 cup | 38% DV (35mg) |
| 9 Jalapeno Peppers | 1 pepper | 18% DV (17mg) |
| 10 Saffron | 1 tbsp | 2% DV (2mg) |
Vitamin C Requirements By Age and Gender
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for Vitamin C ranges from 15mg to 120mg per day. The daily value for vitamin C is 90mg per day. (7)
| Life Stage | RDA |
|---|---|
| Infants* | |
| 0-6 months old | 40mg |
| 7-12 months old | 50mg |
| Children | |
| 1-3 years old | 15mg |
| 4-8 years old | 25mg |
| Males | |
| 9-13 years old | 45mg |
| 14-18 years old | 75mg |
| 19-50 years old | 90mg |
| 50+ years old | 90mg |
| Females | |
| 9-13 years old | 45mg |
| 14-18 years old | 65mg |
| 19-50 years old | 75mg |
| 50+ years old | 75mg |
| Pregnancy | |
| 14-18 years old | 80mg |
| 18+ years old | 85mg |
| Lactation | |
| 14-18 years old | 115mg |
| 18+ years old | 120mg |
Source: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C.
About the Data
Data for the curated food lists comes from the USDA Food Data Central Repository.
You can check our data against the USDA by clicking the (Source) link at the bottom of each food listing.
Note: When checking data please be sure the serving sizes are the same. In the rare case you find any difference, please contact us and we will fix it right away.
About Nutrient Targets
Setting targets can provide a guide to healthy eating.
Some of the most popular targets include:- Daily Value (%DV) - The daily value (%DV) is a general guideline for consumption that will prevent deficiency of a particular nutrient in most people. The %DV refers to the percentage of an amount that's found in a single serving of a food. It also accounts for absorption factors. It is set by the U.S. FDA.
- Recommended Dietary Allowance (%RDA) - The RDA sets an average daily dietary intake level that is sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97.5%) healthy individuals. It's more specific than the daily value, and varies by age and gender. The RDA is set by the US National Instutites of Health.
- Reference Dietary Intake (%RDI) -The reference dietary intake is similar to the recommended daily allowance, but is specific to age and gender. The RDI for amino acids is set by the U.N. World Health Organization.
- Adequate Intake (%AI) - This value is primarily used in reference to omega-3 and omega-6 fats. The Adequate Intake is set by the U.S. Institute of Medicine. Because there is less evidence to determine the ideal targets for consumption of these nutrients, the specific amount is considered to be less reliable. Using the term Adequate Intake, rather than one of the other terms, helps to emphasize that the ideal intake of that particular nutrient has not yet been scientifically determined.
See the Guide to Recommended Daily Intakes for more information.
Want to set your own targets? Sign up for an account and set custom targets in the daily meal planner.From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Vitamin C
- Foods Low in Vitamin C
- Vegetables High in Vitamin C
- Fruits High in Vitamin C
- Vegetarian Foods High in Vitamin C
- Nuts High in Vitamin C
- Beans High in Vitamin C
- Dairy High in Vitamin C
- Breakfast Cereals High in Vitamin C
- Fast Foods High in Vitamin C
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
- Lane DJ, Chikhani S, Richardson V, Richardson DR. Mitochondria, Energy and Cancer: The Relationship with Ascorbic Acid Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1833(6):1527-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Feb 26. 23481043
- Sinclair PR, Gorman N, Shedlofsky SI, Honsinger CP, Sinclair JF, Karagas MR, Anderson KE. Role of Vitamin C in Skin Diseases J Lab Clin Med. 1997 Aug;130(2):197-201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(97)90096-2. 9280147
- Wu SJ, Ng LT, Lin CC. L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) induces the apoptosis of B16 murine melanoma cells via a caspase-8-independent pathway Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Aug 22;518(2-3):96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.06.021. 16054126
- Ströhle A, Wolters M, Hahn A. Vitamin C and Immune Function Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;10(1):54-63. doi: 10.2174/187152811794352105. 21184650
- Yamamoto M. The role of vitamin A and related retinoids in immune function World Rev Nutr Diet. 1991;64:58-84. doi: 10.1159/000418570. 2028624
- Prasad AS. Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells Exp Gerontol. 2008 May;43(5):370-7. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2007.10.013. Epub 2007 Nov 1. 18054190
- U.S.FDA - Daily Value on the New Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels
Try the recipe nutrition calculator, or daily meal planner.
Create a free account to log and track foods.

