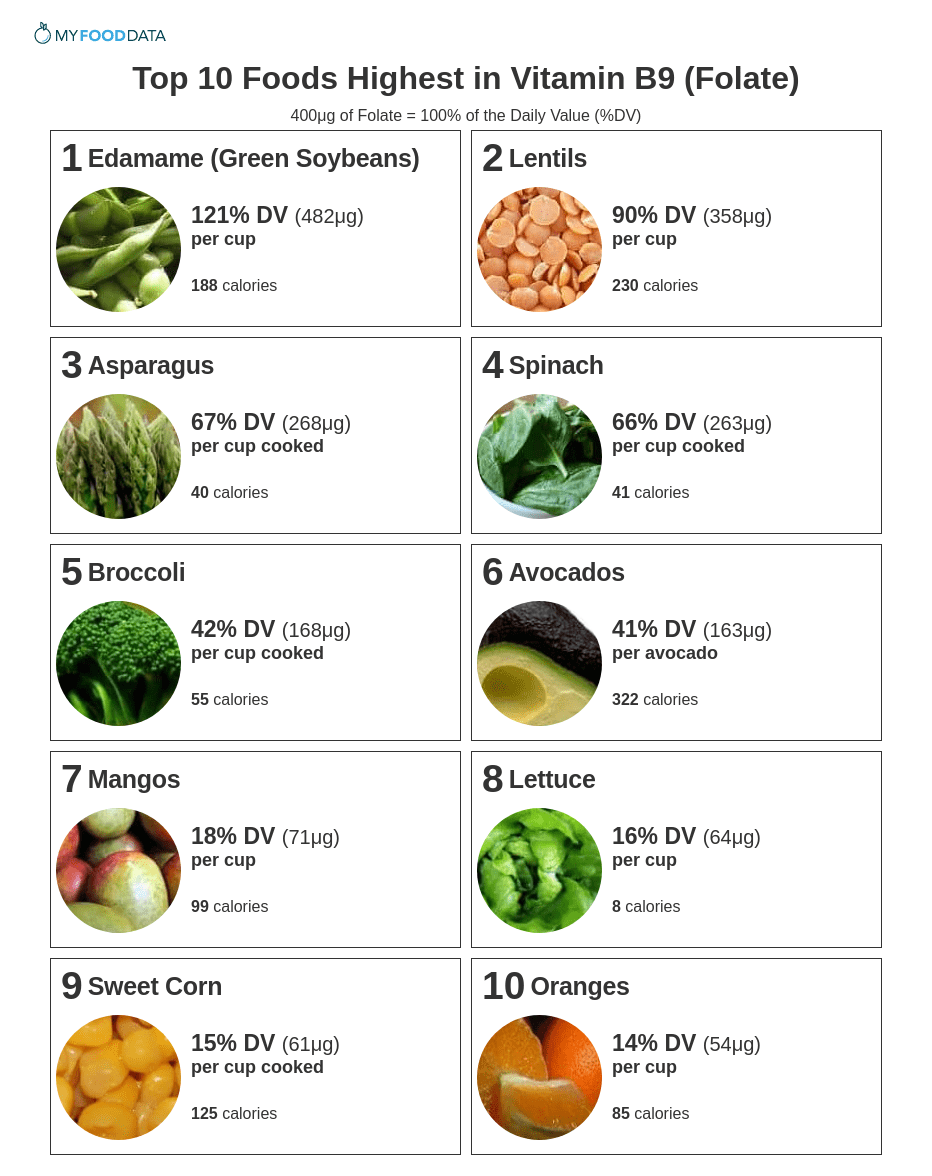
Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B9 (Folate)

Vitamin B9 (folate) is required for numerous body functions, including DNA synthesis and repair, cell division, and cell growth. (1,2)
Folic acid is the synthetic form of vitamin B9 found in fortified foods, like cereals, and supplements.
A deficiency of folate can lead to a form of anemia in adults and slower development in children. For pregnant women, folate is especially important for proper fetal development and preventing neural tube defects. (3)
High folate foods include beans, lentils, asparagus, spinach, broccoli, avocado, mangoes, lettuce, sweet corn, oranges, and whole wheat bread. The current daily value (DV) for folate (Vitamin B9) is 400mcg. (4)
Below are the 10 best foods high in folate. For more see the extended list of folate rich foods, and the complete list of over 200 foods high in folate.
List of High Folate Foods
 1 Edamame (Green Soybeans)
1 Edamame (Green Soybeans)| Folate per Cup | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 482mcg (121% DV) | 311mcg (78% DV) | 514mcg (129% DV) |
More Soy Products High in Folate
- 18% DV in 1 cup of firm tofu
- 12% DV in a 16oz glass of soymilk
 2 Lentils
2 Lentils| Folate per Cup | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 358mcg (90% DV) | 181mcg (45% DV) | 312mcg (78% DV) |
Beans and Pulses High in Folate
- 92% DV in 1 cup of roman beans
- 89% DV in 1 cup of black-eyed peas
- 74% DV in 1 cup of pinto beans
- 71% DV in 1 cup of chickpeas
- 64% DV in 1 cup of black beans
See all beans and pulses high in folate.
 3 Asparagus
3 Asparagus| Folate per Cup Cooked | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 268mcg (67% DV) | 149mcg (37% DV) | 1355mcg (339% DV) |
See all 200 vegetables high in folate.
 4 Spinach
4 Spinach| Folate per Cup Cooked | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 263mcg (66% DV) | 146mcg (37% DV) | 1270mcg (317% DV) |
More Dark Leafy Greens High in Folate
- 42% DV in 1 cup of cooked turnip greens
- 17% DV per cup of cooked Pak Choi
- 8% DV in 1 cup of cooked collard greens
See all 200 vegetables high in folate.
 5 Broccoli
5 Broccoli| Folate per Cup Cooked | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 168mcg (42% DV) | 108mcg (27% DV) | 617mcg (154% DV) |
See all 200 vegetables high in folate.
 6 Avocados
6 Avocados| Folate per Avocado | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 163mcg (41% DV) | 81mcg (20% DV) | 101mcg (25% DV) |
 7 Mangos
7 Mangos| Folate per Cup | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 71mcg (18% DV) | 43mcg (11% DV) | 143mcg (36% DV) |
More Fruits High in Folate
- 20% DV in 1 cup of guavas
- 17% DV in 1 cup of pomegranate
- 13% DV in 1 cup of papaya
- 11% DV in 1 cup of sliced kiwi fruit
- 10% DV in 1 cup of sliced strawberries
See all fruits high in folate.
 8 Lettuce
8 Lettuce| Folate per Cup | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 64mcg (16% DV) | 136mcg (34% DV) | 1600mcg (400% DV) |
More Salad Greens High in Folate
- 18% DV per cup of endive
- 10% DV in 1 cup of butterhead lettuce
- 10% DV in 1 cup of garden cress
See all 200 vegetables high in folate.
 9 Sweet Corn
9 Sweet Corn| Folate per Cup Cooked | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 61mcg (15% DV) | 42mcg (11% DV) | 98mcg (24% DV) |
 10 Oranges
10 Oranges| Folate per Cup | Folate per 100g | Folate per 200 Calories |
|---|---|---|
| 54mcg (14% DV) | 30mcg (8% DV) | 128mcg (32% DV) |
See all fruits high in folate.
Printable One Page Sheet
Extended List of Folate Rich Foods
| Food | Serving | Folate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Lamb Liver (Cooked) | 3oz serving | 85% DV (340mcg) |
| 2 Beef Liver (Cooked) | 1 slice (~3oz) | 53% DV (211mcg) |
| 3 Caned Baked Beans with Beef | per cup | 29% DV (114mcg) |
| 4 Spinach Egg Noodles (Cooked) | per cup | 26% DV (102mcg) |
| 5 Roasted Chestnuts | per cup | 25% DV (100mcg) |
| 6 Cooked White Rice | per cup | 23% DV (92mcg) |
| 7 Duran | per cup chopped | 22% DV (87mcg) |
| 8 Cooked Quinoa | per cup | 19% DV (78mcg) |
| 9 Firm Tofu | per cup | 18% DV (73mcg) |
| 10 Canned Blue Crab | per cup | 17% DV (69mcg) |
| 11 Dry Roasted Sunflower Seeds | per oz | 17% DV (67mcg) |
| 12 Cooked Blue Mussels | per 3oz serving | 16% DV (65mcg) |
| 13 Yellow Cornmeal (Grits) | per cup | 16% DV (63mcg) |
| 14 Cooked Atlantic Salmon (Farmed) | per 6oz serving | 14% DV (58mcg) |
| 15 Cooked Teff | per cup | 11% DV (45mcg) |
| 16 Cooked Wild Rice | per cup | 11% DV (43mcg) |
| 17 Cooked Dungeness Crab | per 3oz | 9% DV (36mcg) |
| 18 Cooked Bulgur | per cup | 8% DV (33mcg) |
| 19 Egg Yolks | 1 large yolk | 6% DV (25mcg) |
| 20 Whole Milk | per 16oz glass | 6% DV (24mcg) |
How Much Vitamin B9 (Folate) Do You Need?
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for folate (B9) ranges from 150mcg to 600mcg per day. The daily value for vitamin B9 is 400mcg per day. (4)
| Life Stage | RDA |
|---|---|
| Infants* | |
| 0-6 months old | 65mcg |
| 7-12 months old | 80mcg |
| Children | |
| 1-3 years old | 150mcg |
| 4-8 years old | 200mcg |
| Males | |
| 9-13 years old | 300mcg |
| 14-18 years old | 400mcg |
| 19-50 years old | 400mcg |
| 50+ years old | 400mcg |
| Females | |
| 9-13 years old | 300mcg |
| 14-18 years old | 400mcg |
| 19-50 years old | 400mcg |
| 50+ years old | 400mcg |
| Pregnancy | |
| 14-18 years old | 600mcg |
| 18+ years old | 600mcg |
| Lactation | |
| 14-18 years old | 500mcg |
| 18+ years old | 500mcg |
Source: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin B9 (Folate).
Health Benefits of Folate (Vitamin B9)
- Protection Against Heart Disease - Adequate levels of vitamin B9, B6, and B12 have been shown to lower levels of an amino acid in the blood called homocysteine. Lower levels of homocysteine have been shown to improve endothelial function, which in turn may boost cardiovascular health and decrease risk of heart attacks and strokes. (5)
- Protect and Repair DNA to Reduce Cancer Risk - Folate (Vitamin B9) is essential for the maintenance and repair of DNA, which helps to prevent cancer. Several studies have associated diets low in folate with increased risk of breast, pancreatic, and colon cancer. (5,6)
- Decreased Risk of Alzheimer's Disease - Studies suggest that consuming adequate amounts of vitamin B9 (Folate) over a period of at least 10 years results in a decreased risk of Alzheimer's Disease. (7,8)
People at Risk of a Folate (Vitamin B9) Deficiency
- Alcoholics - Alcohol interferes with absorption of folate and increases excretion of folate via the kidneys. (9)
- Pregnant and Lactating Women - Women who are about to become, or are, pregnant need to be sure they have adequate folate in order to reduce risk of premature births, underweight births, and neural tube defects in their infants. (3)
- People with Malabsorption - People with gastrointestinal conditions like tropical sprue, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease may have poor folate absorption in the gut. Even if they consume adequate folate, they may not absorb enough of it to meet their body's needs. (10,11,12)
- People with the MTHFR polymorphism - MTHFR is a gene that's involved in folate processing in the body. There are rare variants of this gene that significantly reduce the body's ability to process folate, which can lead to a variety of health issues. However, many common variants of this gene have only a small effect on folate processing, and have not been shown to have an impact on your health. Because of this, commercially available MTHFR genetic testing generally doesn't provide any information that's useful for improving your health. (13,14)
Folate and Vitamin B12
Other Vitamin B Foods
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Thiamin (Vitamin B1)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Niacin (Vitamin B3)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B6
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B9 (Folate)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
About the Data
Data for the curated food lists comes from the USDA Food Data Central Repository.
You can check our data against the USDA by clicking the (Source) link at the bottom of each food listing.
Note: When checking data please be sure the serving sizes are the same. In the rare case you find any difference, please contact us and we will fix it right away.
About Nutrient Targets
Setting targets can provide a guide to healthy eating.
Some of the most popular targets include:- Daily Value (%DV) - The daily value (%DV) is a general guideline for consumption that will prevent deficiency of a particular nutrient in most people. The %DV refers to the percentage of an amount that's found in a single serving of a food. It also accounts for absorption factors. It is set by the U.S. FDA.
- Recommended Dietary Allowance (%RDA) - The RDA sets an average daily dietary intake level that is sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97.5%) healthy individuals. It's more specific than the daily value, and varies by age and gender. The RDA is set by the US National Instutites of Health.
- Reference Dietary Intake (%RDI) -The reference dietary intake is similar to the recommended daily allowance, but is specific to age and gender. The RDI for amino acids is set by the U.N. World Health Organization.
- Adequate Intake (%AI) - This value is primarily used in reference to omega-3 and omega-6 fats. The Adequate Intake is set by the U.S. Institute of Medicine. Because there is less evidence to determine the ideal targets for consumption of these nutrients, the specific amount is considered to be less reliable. Using the term Adequate Intake, rather than one of the other terms, helps to emphasize that the ideal intake of that particular nutrient has not yet been scientifically determined.
See the Guide to Recommended Daily Intakes for more information.
Want to set your own targets? Sign up for an account and set custom targets in the daily meal planner.From the Nutrient Ranking Tool
Use the ranking tool links below to select foods and create your own food list to share or print.
- Foods High in Folate (B9)
- Foods Low in Folate (B9)
- Vegetables High in Folate (B9)
- Fruits High in Folate (B9)
- Vegetarian Foods High in Folate (B9)
- Nuts High in Folate (B9)
- Grains High in Folate (B9)
- Beans High in Folate (B9)
- Dairy High in Folate (B9)
- Breakfast Cereals High in Folate (B9)
- Fast Foods High in Folate (B9)
View more nutrients with the nutrient ranking tool, or see ratios with the nutrient ratio tool.
Related
Data Sources and References
- Shuaibi AM, House JD, Sevenhuysen GP. The importance of folic acid J Am Diet Assoc. 2008 Dec;108(12):2090-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2008.09.007. 19027414
- Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Folic acid - importance for human health and its role in COVID-19 therapy Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. 36321557
- Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Folic Acid Deficiency Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. 36321557
- U.S.FDA - Daily Value on the New Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels
- Brantigan CO. Folic acid fortification of the food supply. Potential benefits and risks for the elderly population JAMA. 1997 Mar 19;277(11):884-5. 9062324
- Kono S, Chen K. Folic acid and colorectal cancer prevention: molecular mechanisms and epidemiological evidence (Review) Cancer Sci. 2005 Sep;96(9):535-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00090.x. 16128738
- Morris MC, Evans DA, Schneider JA, Tangney CC, Bienias JL, Aggarwal NT. Reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease with high folate intake: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging J Alzheimers Dis. 2006 Aug;9(4):435-43. doi: 10.3233/jad-2006-9410. 16917153
- Rieder CR, Fricke D. Vitamin B(12) and folate in relation to the development of Alzheimer's disease Neurology. 2001 Nov 13;57(9):1742-3. doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.9.1742-a. 11706137
- Halsted CH, Villanueva JA, Devlin AM. Metabolic interactions of alcohol and folate Alcohol. 2002 Jul;27(3):169-72. doi: 10.1016/s0741-8329(02)00225-2. 12163145
- Tropical Sprue
- Theethira TG, Dennis M, Leffler DA. Appropriate nutrient supplementation in celiac disease Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Feb;8(2):123-9. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2014.876360. 24417260
- Yakut M, Ustün Y, Kabaçam G, Soykan I. Associations between Folate and Vitamin B12 Levels and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis Eur J Intern Med. 2010 Aug;21(4):320-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2010.05.007. Epub 2010 Jun 8. 20603044
- Kapiszewska M, Kalemba M, Wojciech U, Milewicz T. The Role of Folate and MTHFR Polymorphisms in the Treatment of Depression J Nutr Biochem. 2005 Aug;16(8):467-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.01.018. 16043029
- Wang Y, Liu Y, Ji W, Qin H, Wu H, Xu D, Turtuohut T, Wang Z. MTHFR genetic testing: Controversy and clinical implications Metab Brain Dis. 2015 Aug;30(4):1017-26. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9662-4. Epub 2015 Apr 10. 25855017
- Smith AD. Folate and vitamin B-12 status in relation to anemia, macrocytosis, and cognitive impairment in older Americans in the age of folic acid fortification Am J Clin Nutr. 2007 Jan;85(1):3-5. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/85.1.3. 17209170
Try the recipe nutrition calculator, or daily meal planner.
Create a free account to log and track foods.

